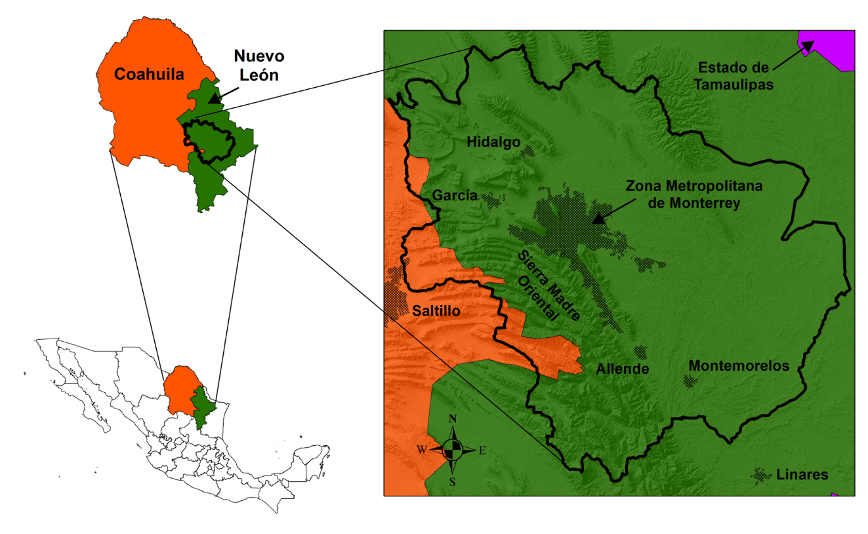
According to information from INEGI (National Institute of Statistics and Geography), the metropolitan area of Monterrey is made up of 18 municipalities, which from 1990 to 2020 have had a growth of 97% (from 2,704,299.00 inhabitants to 5,336,800.00 inhabitants). A growing population, a naturally arid climate, extreme weather events and a limited water management plan during the last decades have severely impacted the water resource, affecting the availability and quality of groundwater and surface water sources in the metropolitan area of Monterrey, Nuevo León, Mexico.
Water scarcity became evident during the spring-summer period of 2022 when an unprecedented drought decreased surface water sources, forcing the state government to take contingency measures and seek water supply alternatives in the city such as reducing the flow of supply, getting administratively available water, drilling new supply wells, and providing users with water in tanker trucks to fill the resource deficit, among other measures.
The methodology proposed in this study is the elaboration of a hydrogeomorphological map that allows to identify and delimit the priority areas of rainwater recharge to the aquifer. This map will relate surface and groundwater dynamics that are influenced by criteria such as geology, rock fracturing density, geomorphology, slopes and topography, surface drainage density (hydrology), conceptual hydrogeological model, vegetation and land use, soil science and precipitation density.
Read here the latest news about the project.







Responses